Unit Ii Review Apã‚â® Exam Practice Questions Multiple Choice Psych
Answers and Review for Multiple Choice Practice on Biological Bases of Beliefs
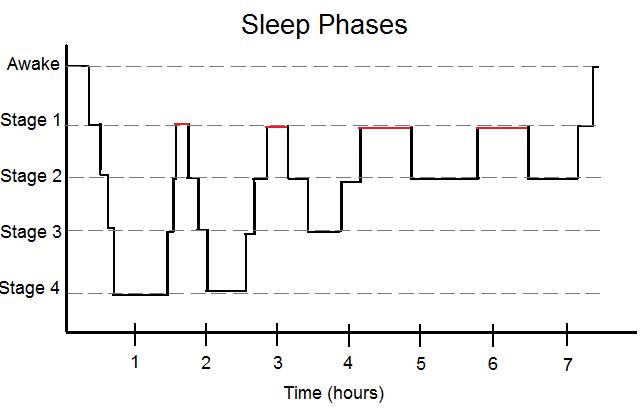
Image Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
Every 90 minutes, nosotros cycle through the four slumber stages: 1-2-3-2-ane-REM, then restart.
⛔STOP!⛔ Before y'all look at the answers brand sure y'all gave this practice quiz a try then you lot can assess your understanding of the concepts covered in unit 2. Click hither for the practice questions:
AP Psychology Unit 2 Multiple Choice Questions.
Facts about the test: The AP Psychology exam has 100 multiple choice questions and you will be given 1 hour and 10 minutes to consummate the section. That means it should take you around 11 minutes to complete xv questions.
Resource:
*The following questions were not written by CollegeBoard and although they cover data outlined in the AP Psychology Class and Exam Description, the formatting on the exam may be different.
one. Mariel was in a auto blow and suffered damage to her reticular formation. Which of the following is she virtually likely experiencing?
A. Convulsive Seizures
B. A Coma
C. Inability to Make New Memories
D. Modify in her Personality
Answer: The reticular germination, located in the old brain, plays an important office in arousal--our natural sleep-wake cycle.
📄 Report AP Psychology, Unit 2.6:
The Encephalontwo. Afterward suffering a stroke, Manny lost his power to cover linguistic communication. It is most likely that Manny suffered damage to
A. His right temporal lobe
B. His hippocampus
C. Wernicke'due south Area
D. Broca's Expanse
Answer: Wernicke's area, located in the left temporal lobe, is responsible for language comprehension.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 2.vi: The Brain
3. The somatosensory cortex is to the ______ lobe as the motor cortex is to the _______lobe.
A. Parietal; frontal
B. Occipital; frontal
C. Frontal; temporal
D. Parietal; temporal
Reply: The somatosensory cortex is located in the parietal lobe; the motor cortex is located in the frontal lobe
📄 Written report AP Psychology, Unit two.half dozen: The Brain
4. Polarization is to __________ as depolarization is to _______.
A. Action potential; resting potential
B. Resting potential; refractory flow
C. Resting potential; action potential
D. Activity potential; refractory period
Answer: When a neuron is stimulated, gates are opened to allow for positively charged sodium ions to flood in, causing depolarization of the axon. This is called an action potential. As the activity potential moves downward the axon, sodium/potassium pumps restore the axon to its original land, that is is is polarized. This is called the resting potential.
📄 Written report AP Psychology, Unit 2.four:
Neural Firing5. Juan was bit by a black widow spider. The venom is an agonist for ACh. What is Juan likely to be experiencing?
A. Paralysis
B. Migraine Headaches
C. Insomnia
D. Musculus spasms
Answer: ACh, or acetylcholine, is i of the best-understood neurotransmitters and can be found at every junction between motor neurons and skeletal muscles. Information technology enables muscle movement, and also plays a role in learning and memory. An antagonist is a molecule that enhances a neurotransmitter's action. The spider venom enhanced Jaun's musculus deportment, resulting in spasms
📄 Report AP Psychology, Unit 2.4: Neural Firing
6. Night terrors are to ________ as hypnagogic sensation are to __________.
A. Stage 3; Stage ane
B. REM sleep; REM sleep
C. REM Slumber; NREM sleep
D. Phase 4; Stage 2
Respond: Night terrors, which are different than nightmares that occur during REM sleep, occur during Stage 3--about 2 or 3 hours after falling asleep. Hypnagogic sensations refer to the jerking or sudden feeling of falling that occur right when you are falling asleep ( Stage 1)
📄 Report AP Psychology, Unit of measurement 2.nine: Sleep and Dreaming
7. What is the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
A. It increases the production of dopamine, causing us to experience pleasure
B. It blocks messages between our motor cortex and brainstem, causing paradoxical sleep
C. It suppresses the pineal gland'southward production of melatonin, causing us to awaken
D. Information technology interferes with our natural cyclic rhythms, causing insomnia
Reply: The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) reacts to low-cal striking the retina. This sends a signal to the SCN to suppress the product of melatonin. At dark, the SCN quiets down, which allows for the release of melatonin and thus the feeling of sleepiness.
📄 Written report AP Psychology, Unit ii.nine: Sleep and Dreaming
8. Aiko has been struggling with depression and finds it difficult to concentrate on her school work. It is virtually likely that Aiko has a shortage of which neurotransmitter?
A. GABA
B. Dopamine
C. ACh
D. Serotonin
Answer: Serotonin affects our mood, hunger, sleep and arousal and an undersupply has been linked to depression. Prozac and other antidepressant drugs enhance serotonin levels by blocking their re-uptake or chemic breakup
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit ii.4:
Neural Firing9. Neurotransmitters receptor sites are located on the
A. Soma
B. Dendrites
C. Axon
D. Terminal Branches
Respond: Dendrites are the neuron's branching extensions that receive the neurotransmitters and send the message (impulse) toward the prison cell body (soma). Neurotransmitters fit into the receptor cells much like a primal fits into a lock.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit of measurement ii.four: Neural Firing
ten. Your ability to swat at a fly buzzing around your head is due to your
A. Somatic nervous organization
B. Autonomic nervous system
C. Parasympathetic nervous system
D. Endocrine organization
Answer: The somatic nervous system is part of the peripheral nervous system. It is responsible for gathering information and directing key nervous system decisions to your body parts.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 2.iii: Overview of the NS and the Neuron
11. The "uncommitted" areas of the cerebral cortex that are involved in higher-lodge cognitive functions and are more pervasive in more intelligent animals are called
A. Hemisphere lobes
B. Cortex interfaces
C. Association areas
D. Wernicke'south expanse
Answer: Association areas are involved in functions that make us human such equally learning, remembering, thinking and speaking. The fact that and so much of our brain is "uncommitted," has led to the myth that nosotros merely use x% of our brains.
📄 Written report AP Psychology, Unit 2.6:
The Brain12. The role of the brain that links the nervous and endocrine systems is the
A. Pituitary Gland
B. Thalamus
C. Hypothalamus
D. Hormones
Answer: The hypothalamus, located in the limbic system just below (hypo) the thalamus, is responsible for maintaining homeostasis in our bodies. It secretes hormones that transport letters to the pituitary gland (the main gland) that in turn sends messages to all of the other glands in the endocrine organisation to release their hormones into the bloodstream.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit of measurement ii.2: The Endocrine System
13. What can be expected in someone who has been a long-term user of the drug Ecstasy?
A. An increased production of dopamine, resulting in hallucinations
B. Damaged serotonin-producing neurons, leading to depression
C. Reduced dopamine levels, resulting in depression
D. Decreased product of endorphins, leading to lower pain thresholds
Answer: Ecstasy, also known every bit MDMA or "Molly," is a stimulant and balmy hallucinogen. Information technology triggers dopamine release and blocks the reuptake of serotonin resulting in a experience-skilful rush of emotions and a feeling of connection with those effectually you. In addition to the damage to serotonin-producing neurons, Ecstasy also suppresses the nervous organization, impairs memory and can disturb the sleep bike.
14. Which of the following technologies would be most useful for determining what phase of slumber someone is in?
A. MRI
B. fMRI
C. PET Scan
D. EEG
Answer: An EEG, or electroencephalogram, amplifies the electrical activity of the brain'due south surface. Researchers are able to measure the waves by placing electrodes on the scalp. Each stage of slumber has a different type of wave associated with information technology (e.thousand. alpha, theta, delta).
xv. If a trait is found to be 85% heritable, what does that mean?
A. Information technology means that you are highly likely to inherit that trait if it is passed down to you past your parents
B. It ways that 85% of that trait comes from your genes and xv% from your experiences
C. It ways that 85% of the variation of that trait amongst individuals in a grouping tin can be attributed to genes
D. It ways that 85% of that trait can be attributed to your experiences and 15% to your genes
Answer: Heritability is often confused with the concept of inherited, but they are very different. Heritability is calculated by behavioral geneticists--oftentimes through their studies of identical twins. It is a statistical measure and refers to the proportion of variation among individuals in a group that can exist attributed to genetic makeup. If a trait is 85% heritable, it means that genetic influence explains about 85% of the variation amid people--not that 85% of that trait the trait is 85% genetic.
What can we help you do now?
🤝Connect with other students studying AP Psychology with
HoursResources:
Source: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-psych/unit-2/mc-answers-review/study-guide/pXuxN8oWgBTxU1iDIHki
0 Response to "Unit Ii Review Apã‚â® Exam Practice Questions Multiple Choice Psych"
Post a Comment